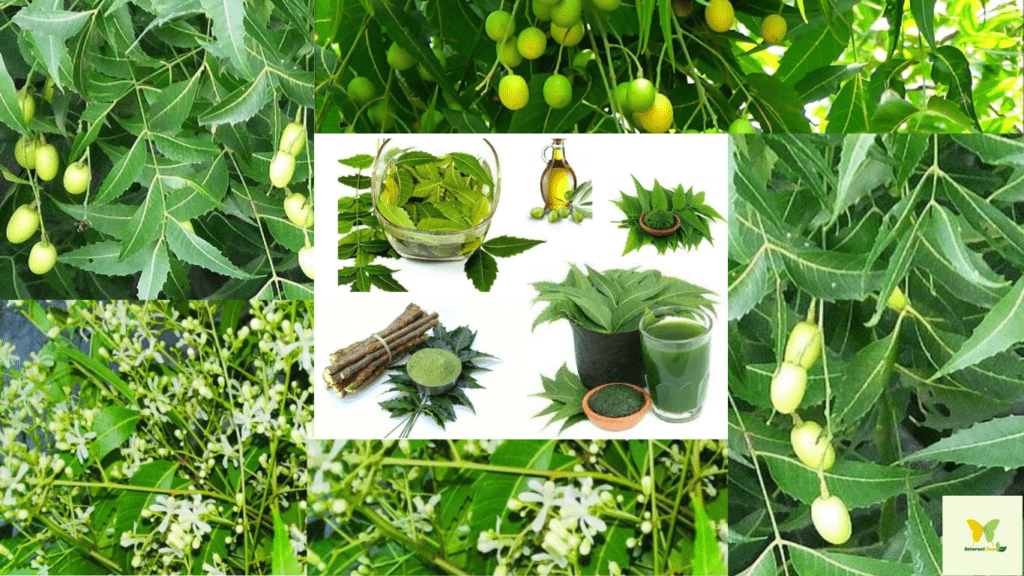
The Neem Tree, also known as Azadirachta indica A.Juss., is a wonderful medicinal plant found in the Indian subcontinent, including countries like India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Nepal. It is often called the “village pharmacy” for its wide range of medicinal properties that make it a part of daily life in these regions. The tree offers so much – from its branches, leaves, and juice used in traditional medicine, organic pesticides, to its valuable wood. Neem, an evergreen tree, thrives in arid and semi-arid regions, and has also been introduced to parts of Africa, the Caribbean, and several countries in South and Central America. Its versatile applications include use in Ayurvedic medicine, folk medicine, cosmetics, and organic farming.
Table of Contents
TogglePlant Description
The neem tree is a real gem of a plant! It can grow to be 15–30 m (49–98 ft) tall with a lovely rounded crown and thick, hairy bark. Its compound leaves have toothed leaflets and are usually evergreen, except during extreme drought. You’ll be delighted by the small, fragrant white flowers – they’re bisexual or staminate (male) and grow in clusters in the leaf axils. And don’t even get me started on the fruit – it’s a smooth yellow-green drupe with a sweet-smelling pulp! Neem is pretty easy to grow from seed, and you can also propagate it from cuttings or root suckers. This hardy and resilient plant does well in poor, rocky soils, and it’s not too fussy about environmental conditions – although it can’t handle freezing temperatures or waterlogged soil. Plus, get this – neem trees can live for over 200 years. Talk about long-lasting and resilient!
The Neem Tree is of great importance
Neem trees are really amazing! They are considered sacred and are associated with many influential thinkers around the world. Neem trees offer so many benefits, such as helping to alleviate poverty and create jobs. They’re also great for health, as their wood is resistant to infections and neem-based products don’t cause skin cancer. Plus, they provide cool shade, have antiviral properties, and can even help reduce pest infestation on farmlands. The World Health Organization has even declared neem as the ‘tree of the 21st century.’ Neem-based products like medicines, cosmetics, fertilizers, and insect repellents are loved worldwide. It’s incredible that every part of the neem tree, from its leaves to its wood, is exportable. Neem trees live for over 400 years and don’t harm cows or goats. They are also environmentally friendly, acting as a biopesticide and fertilizer that doesn’t harm beneficial insects or bacteria. On top of all that, neem oil can be used to light lamps, making it a truly valuable tree in the world.
Ecological Importance
The neem tree is crucial for maintaining ecological balance. Its dense foliage provides shade, preventing soil erosion and desertification, and protecting the soil from harsh sunlight. The tree’s flowers attract pollinators, fostering a diverse insect population. When neem leaves fall and decompose, they enrich the soil with organic matter and nutrients. Neem also helps control pollution resulting from industrial activities. Moreover, it protects against storms and river erosion, prevents soil salinity, and balances soil acidity and alkalinity. Additionally, the neem tree helps keep the air cool, with temperatures under the tree typically 1-2 degrees lower than those under other trees.
Nutritional Value
Neem leaves are full of nutrients and bioactive compounds, like vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and flavonoids, that are great for your overall health and energy levels. People often enjoy neem leaves as herbal tea or add them to their favorite dishes. Neem flower honey is more nutritious and medicinal compared to other types of flower honey.
Chemical Constituents
Neem bark, flowers, fruits, seeds, and oil contain a variety of bitter compounds such as saponins, alkaloids (nimbidine, nimbon, nimbinin, nimbdol), triterpenoids, salnin, azadirachtin, organic acids, melianone, nimbolide, quercetin, glycosides, tannin, and margocin. These natural ingredients have many beneficial properties.
Neem Trees Beside the House
They say that having two to four neem trees planted around your house can reduce your insurance costs, keep you healthy, and help you relax better when resting or sleeping lying down.
Seed Collection and Sowing the Seeds
Neem seeds are usually collected between June and August at the beginning of the monsoon season in Aamd countries. They are neither too big nor too small, with about 1500 to 1800 seeds per kilogram. The seeds should be collected directly from the tree or from under the tree. In April and May, mature neem trees produce small fragrant white flowers, followed by yellow ovoid mature fruits in June and July. Each fruit contains one seed. The seeds should be spread and dried in the shade, then sown in potting soil within three weeks. The sowing of seeds can begin after June 30, and seedlings typically germinate within 7 to 10 days. The germination rate is 70 to 80 percent. It is also possible to sow the seeds in nursery beds, polythene, or directly in the ground. Soaking the seeds in cold or lukewarm water can increase their germination capacity.
Planting
It’s best to go for 1-year-old seedlings. Before planting, make sure to give the stem a little trim if needed. September is an ideal time to plant the seedlings. When planting, mix 25-30 kg of organic manure, 50 g of TSP, and 50 g of MOP thoroughly with the soil in 45 cm wide pits. Once the seedlings are in the ground, be sure to water them regularly and moderately. It’s also important to elevate the ground and fence it with a cage until the plants are as tall as a human being. Give them some special care during this stage!
Care
If you’re interested in growing neem trees, here’s some helpful advice:
Neem trees are commonly found in open areas and can grow in various types of soil, including sandy and loamy soils, along roadsides, plains, and in temperate climates. They bloom from March to May, and their fruits ripen from June to August. It’s important to collect the seeds during this time and plant them in bags or pots within 2-3 weeks of collection to ensure they grow well. When the neem saplings are a year old, you can transplant them to the main land. The best time to plant neem seedlings is during the monsoon season on weed-free and clean land, while ensuring the base of the tree is elevated to prevent dew accumulation. After planting, make sure to fence the area to protect the seedlings from animals and humans. If you encounter issues like scale insects or fungi, seeking expert advice is the way to go.
Collection and Storage Method
Please follow these steps for collecting and storing neem leaves and seeds:
- Collect the neem leaves and clean them.
- Dry the leaves in the sun until they become slightly darker and the moisture content decreases.
- Pack the dried leaves and label the packets with proper identification guidelines for marketing.
- Neem fruit ripens between June and August. Collect the seeds when they are mature. To prevent the seeds from falling on the ground, you can tie a thick net around the tree. This will help in saving all the seeds.
- Wash the seeds and dry them in the sun until the humidity is reduced to 2 percent.
- Once dried, store the seeds in airtight packets.
- Peel the neem fruit, cut it into pieces, wash thoroughly, dry in the sun, and store in an airtight container.
Uses
Neem is a very beneficial tree for us. It has been popular since time immemorial. Every part of the neem tree, from the leaf to the bark, from the root to the flower, and from the fruit to the seed, has its uses. Many of its medicinal and cosmetic uses are based on its antibacterial and antifungal properties.
- Neem is commonly used in shampoos to treat dandruff, and in soaps or creams for skin conditions such as acne, psoriasis, and athlete’s foot. It is also an ingredient in some toothpastes and mouthwashes. Neem pods are traditionally used as a natural toothbrush due to their antibacterial properties, especially in the Indian subcontinent. The young stems are directly used as unrefined toothbrushes in rural areas.
- Neem-leaves have long been used as a traditional treatment for diabetes, and there is some clinical evidence that it can help control blood sugar levels.
- A paste made from neem leaves can be applied to wounds caused by injuries or insect bites several times a day to promote quick healing.
- Crushing some neem leaves and mixing them with a glass of water and drinking it every morning can boost immunity manifold.
- Neem-flowers are used as an appetite suppressant, for treating nausea, colic, and intestinal worm infections. In addition, neem flowers are also used as medicine for eye and skin diseases and headaches. Neem flowers are used in aromatherapy for their cooling properties.
- The oil extracted from neem seeds can be used directly as an insecticide and fungicide against insects and mites. It is also the source of many commercial pesticide products, including dusts, granules, and concentrates. The primary active insecticide ingredient, azadirachtin, disrupts hormones involved in insect molting, prevents larvae from developing properly into adults, and acts as a feeding deterrent. Neem-oil can kill soft-bodied insects on contact and reduce mating and reproductive behavior, thus reducing insect fertility. As a fungicide, neem oil is used to control rust, black spot, scab, anthracnose, and blight. Neem oil breaks down quickly when exposed to UV light, so repeated applications are required. Neem-based pesticides are generally less toxic to mammals and are common in organic agricultural applications.
- As the neem tree matures, its pulp is used to make furniture. Neem wood is also used to make window and door frames.
Warning
Neem oil, neem bark, and leaves are unsafe for pregnant women to consume and can cause miscarriage.