Many people are interested in having a fruit garden. Taking some preparatory measures before starting a fruit garden can make it easier to see future profits. Additionally, increasing the number of fruit gardens in the country can reduce the need to import fruits from abroad, and can even provide an additional source of income.
Please remember the following instructions for planting a fruit garden:
Table of Contents
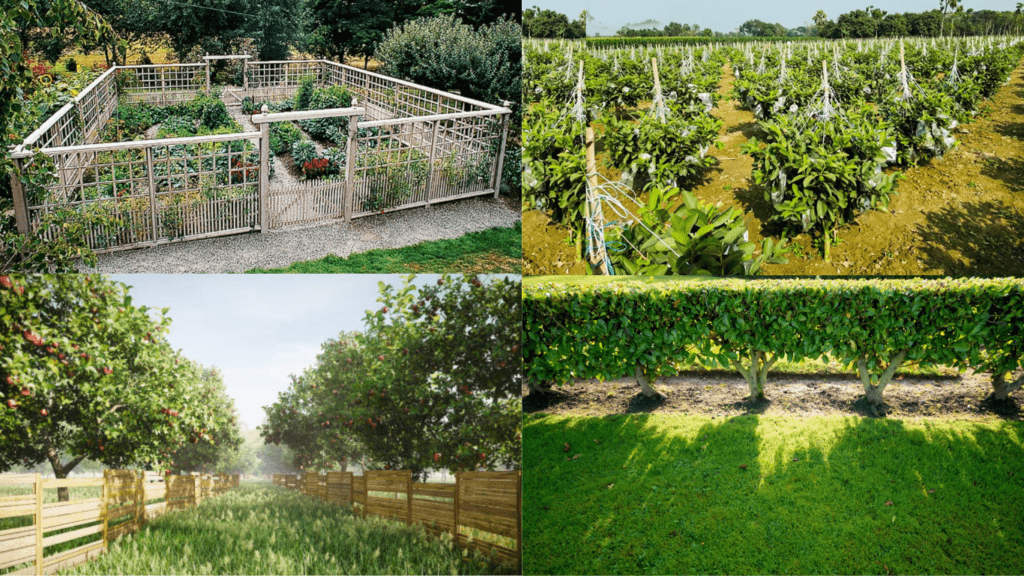
ToggleWall, Fence or Hedge:
To protect the garden overall, along with preparing the land, it’s important to construct a permanent fence around the garden area, or even a concrete wall. A bamboo fence around each plantation can immediately protect the trees from animals such as cows and goats. However, mixed orchards are a long-term project.
The garden needs to be fenced to protect it from various pests. Permanent fences are brick-built, temporary fences are made of bamboo gates, and hedges or living fences are made of trees. Living fences last longer and can be done at a low cost. Barbed wire fences can be placed along the boundary on the outside, and hedge trees can also be planted directly. Concrete-encased casing or geotextile poles can be installed to carry the barbed wire. Hedge plants are best if they are bushy, suitable for pruning, evergreen, goat-free, low-maintenance, and resistant to insects and diseases. Suitable plants for high hedges include durant, thorn-henna, shaora, karanja, and kamini, while justicia, lantana, acalypha, rangan, patabahar, and kochia are suitable for low hedges.
Hedge Production and Conservation:
For hedges, three rows of seeds should be sown or grafted. After the plants reach a height of about 30 cm, the tips above 15 cm above the bark should be cut for the first time. The trees should be bushy and strong at the beginning by pruning as necessary every few days. Regular fertilization and watering as needed are essential for hedge production and maintenance.
Irrigation and Drainage System:
Sources of irrigation water include shallow tube wells, tube wells, wells, and ponds. Pumps, rubber tubes, and sprinklers are used for irrigation. A nursery or garden should have a good drainage system. Proper elevation and sloping of the land, as well as digging drains at the right places, are necessary for good water drainage.
To ensure the survival of each seedling, it is necessary to irrigate the base of the plant with a little water in the morning and afternoon. Fruit gardening requires long-term commitment and is not advisable for those who think planting a few trees in a row is sufficient. Arboriculture is a long-term endeavor, similar to building with a 100-year plan. Just as water management is important in construction, it is also crucial for orchards.
A good water irrigation system should be in place to address the dry season before the seedlings are properly established. If the seedlings survive and get established before the monsoon, it can provide peace of mind for the garden owner.
Planting Seedlings at the Right Time:
The best time for planting is during summer and early monsoon, which is from April to June. It is advisable to avoid planting in July and August, as heavy rains during this time can cause the seedlings to rot and die. Seedlings can also be planted in September.
Planting in the Right Way:
Before planting the seedlings, it’s important to dig a hole. For most fruit trees, a hole two feet in diameter and depth is suitable. Larger trees like mango, jackfruit, litchi, lemon, etc. require a bigger hole. However, as seedlings are nearly the same size, they can be planted in holes of similar dimensions. Mix 10 kg dung manure, 250 gm TSP, and 100 gm MOP manure with the soil in the pit as starter fertilizer.
Here's a Recommended Method:
Place the topsoil on one side of the pit and the bottom soil on the other side. Leave it open for 10-15 days (or one week) to allow sunlight and air to reach the pit. After mixing the fertilizer with the topsoil, pour the mixture into the lower part of the hole and fill the hole with the remaining soil from the bottom.
If there’s no rain, water the pit the day before planting. Afternoon is the best time for planting. Spread the roots of the seedling well in the hole and gently press them into the soil. Ensure the root of the seedling is buried in the soil up to the place where it was in the previous soil. Gently press the root soil after planting. For the first few days, sprinkle the seedlings with water for root irrigation. Providing shade over the seedlings and covering the root soil with dry grass or straw is beneficial. Six months after planting, you can use some urea fertilizers.